Managing Pay Mix in Global Settings
For multi-national corporations, the sales pay mix (base salary vs. variable incentive) coincides with Geert Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions. Societies that value individualism and encourage risk-taking in business, like the U.S., tend to put more pay at risk for their salespeople; countries that advocate collectivism and avoid uncertainty, like Japan, tend to have less variable incentive for reps. Directors of Sales Operations or HR can use Cultural Dimensions to manage their pay mixes, especially those in the emerging markets, so that they reflect corporate compensation philosophies while conforming to the cultural norms of respective host countries.
Different Pay Mixes for Different Geographies
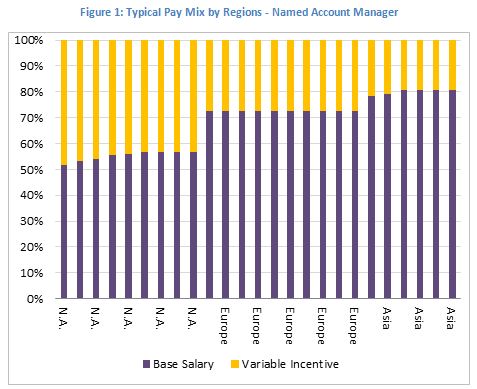
A basic principle in sales compensation design is that the same sales job should have the same pay mix regardless of individual sales reps’ qualifications. For a company operating only in the U.S., this principle can be enforced without much difficulty; for a multi-national company, regional differences dictate that the pay mix needs to have a range. North America often has a more aggressive pay mix than other regions in the world (see below).
Predicting Pay Mix Preferences Using Cultural Dimensions
Pay mix variation reflects different perceptions of compensation fairness across the globe. An American sales rep may consider it normal to have 50% of his/her pay at risk. Such an aggressive pay mix in Europe could be regarded as an unequal treatment of workers – “almost criminal”, as one French sales executive from a Fortune 1000 electronic company put it. In Japan, traditional Japanese companies may not have sales incentive programs at all. Salespeople are paid just as other employees, with a base salary and a corporate bonus at year-end.
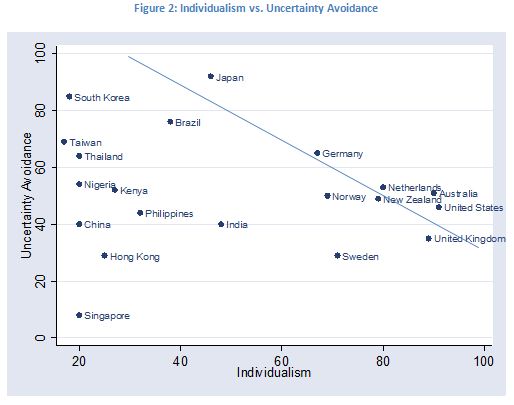
One method of predicting a region’s culturally preferred pay mix is using the Cultural Dimension Theory. Developed in the 1970’s by Geert Hofstede, this theory generalizes the world’s cultural differences into five dimensions, namely: Individualism, Uncertainty Avoidance, Power Difference, Masculinity and Long-Term Orientation. The first two dimensions, i.e., Individualism and Uncertainty Avoidance, are relevant to the question of pay mix preference. The following chart plots the ranking of the world’s major economies on these two cultural dimensions.
Pay mix preferences largely follow these two particular cultural dimensions. Salespeople from societies that value individual performance and have high tolerance for uncertainty (i.e., less risk-averse) tend to prefer aggressive pay mixes. The U.S. is a good example. Societies that value teamwork and have low uncertainty tolerance, such as Japan, tend to have less aggressive pay mixes in favor of stable base salaries and small differences among peers.
Managing Pay Mix Ranges
Therefore, understanding the Culture Dimensions could help directors of sales operations design the right pay mixes for a region. At least, the Cultural Dimensions are useful to predict sales personnel’s reaction to a specific pay mix.
Of course, there are exceptions. For example, some countries are simply too small to merit a unique pay mix even if their Cultural Dimensions are different from surrounding nations. It is necessary to group countries geographically and determine the proper sales pay mix based on their average Culture Dimension values. In the end, there may be only three pay mixes for a job globally – in Americas, EMEA and APAC.
These are the general rules for managing global pay mixes. In reality, the design process will need to take into account many other variables. But it is always useful to have a set of quantitative analysis to support decisions. In this sense, the Cultural Dimension index is an important tool for directors of Sales Ops and HR to keep at their fingertips.
To learn more about the considerations for compensation plans in global markets, visit the compensation and benchmarking practices.