Effective governance: The oil that makes your sales compensation engine run

Every car engine requires oil. Without oil, the engine will start making strange noises and eventually come to a grinding halt. The same can be said for a company’s sales compensation program; without a strong governance infrastructure, the sales compensation program is at risk of breaking down. Engine trouble is often indicated through a variety of indicator lights; ugly sounds that come from under the hood; or, if ignored, when the car dies and you have to call a tow truck. What are the indicators of a poor performing sales compensation program? Consider the following:
- Plans and quotas introduced well after the fiscal year has started
- Excessive questions from the field inquiring about how the plan works
- Frequent crediting and payment disputes with no defined resolution pathway
- Regular finger-pointing between those responsible for program management
As a sales compensation program leader, do you regularly run into these issues? If so, you are not alone. Many sales organizations allocate substantial resources to plan design (building the engine) yet fail to allocate the time and investment necessary to ensure the right systems, policies and processes (the oil) are in place to make the sales compensation program operate smoothly.
A Complete Sales Governance Framework
An effective governance model links together all five phases of the sales compensation program, including:

1) Plan: Capturing critical sales compensation design inputs such as sales strategy & business objectives, sales strategy & coverage model, and sales job roles & responsibilities
2) Design: Working with multiple functional groups to develop plans that align to sales objectives and drive the right behaviors
3) Implement: Setting up targets & territories, crediting rules & policies, and communicating plans to sales incumbents
4) Administer: Calculating and processing payments, providing reports, managing exceptions and resolving disputes
5) Assess: Analyzing plan effectiveness to identify future change requirements
We frequently see breakdowns occur across this chain because organizations fail to emphasize critical governance elements across each of the five phases. Many sales compensation managers find it difficult to address governance challenges head-on, opting instead to solve around the edges by trying to “simplify the plan” or “buy software to help automate the process.” To be clear, simplification and automation are great levers, but they rarely solve root causes of sales compensation program breakdowns.
Building the Solid Governance Model
So what is included in an effective governance model? AGI recommends the following four pieces be put in place:
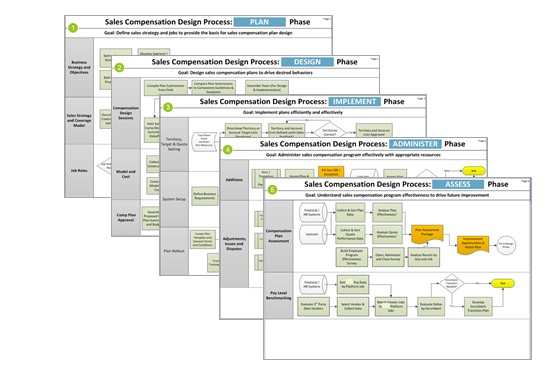
1. An End-to-End Process: Build a comprehensive set of all the execution steps from the Plan phase through the Assess phase. This may sound easy, but after engaging all of those involved with the sales compensation program and mapping out the entire process, bigger companies may have over one hundred unique steps, each requiring time and resources to execute. But once completed, you now have the foundation to execute, with clarity and transparency, all the steps of sales compensation program management. A detailed mapping should look something like this:
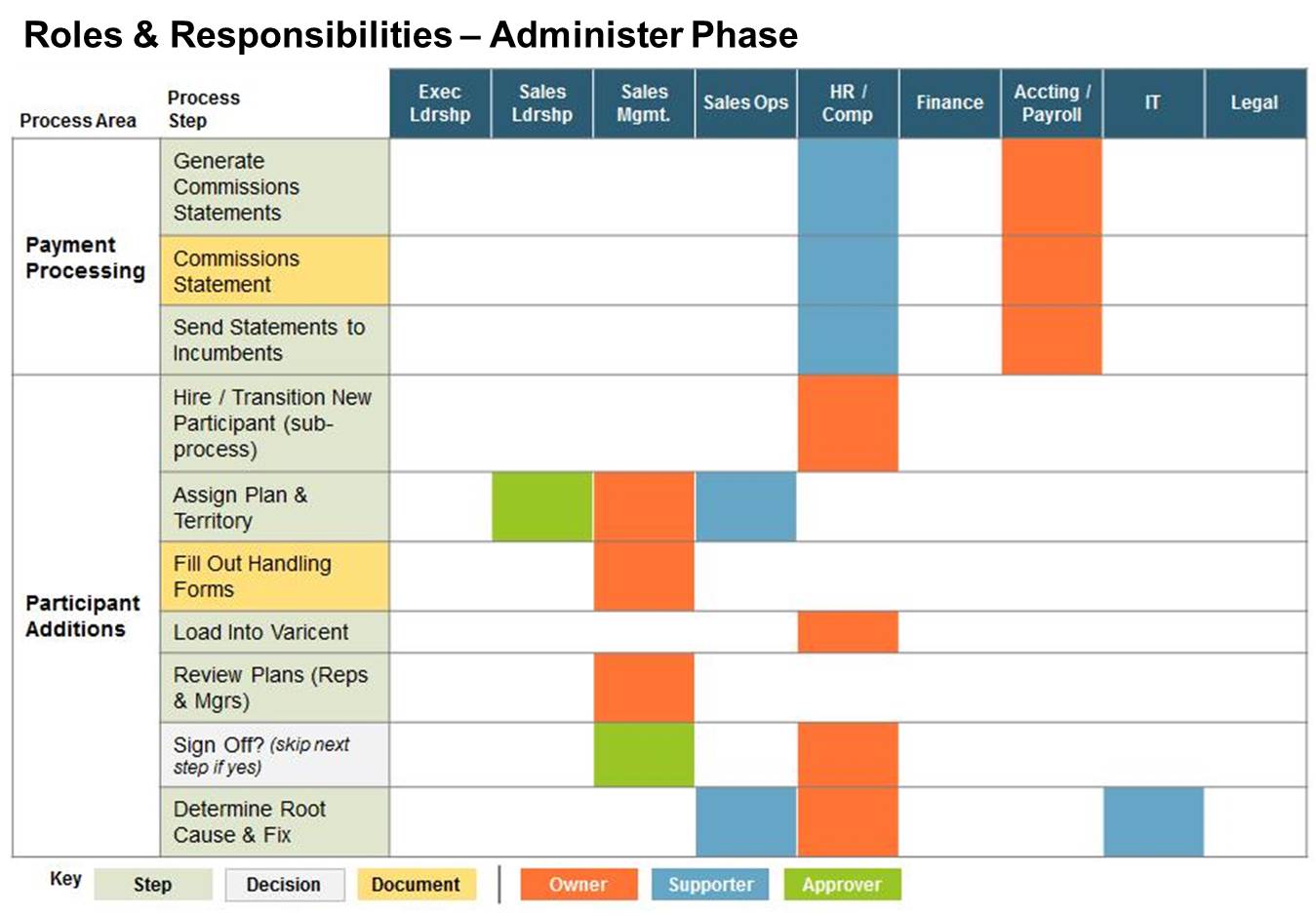
 2. Roles & Responsibilities: The next logical activity is to document the assignment of owners, approvers and supporters by functional group for each step in the end-to-end process. To get agreement on who should be doing what can sometimes prove a challenge because it requires people to commit to do something that may not fall within their traditional job function. But the benefits of having a well thought out RACI matrix can be felt over the short term and long term. Within a specific plan cycle, all participants can be clearly aware of who is doing what so the process moves efficiently. Additionally, when key players transition to new departments or leave the company, replacements can more easily pick things up to ensure the engine keeps running. A best in class RACI matrix covers all program steps. Here is an example:
2. Roles & Responsibilities: The next logical activity is to document the assignment of owners, approvers and supporters by functional group for each step in the end-to-end process. To get agreement on who should be doing what can sometimes prove a challenge because it requires people to commit to do something that may not fall within their traditional job function. But the benefits of having a well thought out RACI matrix can be felt over the short term and long term. Within a specific plan cycle, all participants can be clearly aware of who is doing what so the process moves efficiently. Additionally, when key players transition to new departments or leave the company, replacements can more easily pick things up to ensure the engine keeps running. A best in class RACI matrix covers all program steps. Here is an example:
3. Global Calendar & SLAs: A critical but often overlooked follow-on step to the RACI matrix is its transposition into a global calendar. The timing of activities is equally important as the assignment of owners. If this step is missed, then the probability of engine trouble increases significantly. Consider the situation of a recent Alexander Group client whose program contributors—across Sales, Sales Ops, HR, Finance, Legal, etc.—regularly bickered because functional groups didn’t have shared commitment on the timing of key deliverables. The bickering created distrust, indifference and a delay domino effect ultimately leading to plans being introduced halfway through the year.
An effective global calendar includes all the end-to-end process steps that are sequenced in the right order with specific start and completion times. Many steps within the sales compensation management program rely on outputs from preceding steps; clear ownership and deadlines within necessary time frames help ensure key dependencies associated with each step are handled in an effective manner.
4. Sales Compensation Committees & Escalation Pathways: The last critical piece is the formation of a sales compensation governance committee that meets regularly to address issues such as a) rep performance, b) plan effectiveness, c) plan cost actuals vs. accruals, d) management exceptions, and e) crediting disputes. Large organizations tend to rely on a multi-level committee hierarchy to ensure minor issues are resolved at the local level while senior leadership is brought in to address larger issues that could not be resolved at lower levels. Best-in-class committees come in multiple shapes and sizes; but regardless of how they are structured, these committees share fundamental characteristics including:
- A defined charter with representation from multiple functional groups
- Clear escalation pathways that define the what, when, who and how of issue escalation
- A repository for plan improvement suggestions
A fully-functional governance committee engenders confidence in the sales compensation program because participants know their concerns will be addressed and ideas will be considered for next year’s plan design.
The Importance of An Effective Sales Governance Model
An effective governance model is a prerequisite to effectively scaling a company’s sales compensation program. Building the right infrastructure, including process maps, roles & responsibilities, global calendars and governance committees, can save a lot of time and ensure the sales compensation engine continues to run smoothly.
Contact Us
Do you believe your company can benefit from a governance upgrade? Want to learn more? Visit our website, or peruse our eBook on this subject. Read this related post or contact us today.
