Sales compensation structures play a pivotal role in shaping organizational behavior, driving performance and reinforcing business strategies—and they can be powerful levers for cultural and strategic transformation. When a company restructures its incentive programs, adjusts pay-for-performance models or shifts its approach to sales compensation, employees are directly influenced by these changes. Well-designed sales compensation frameworks steer individuals toward desired behaviors, ensuring alignment with broader corporate goals.
However, significant adjustments to sales compensation require careful change management to ensure that transitions are smooth, resistance is minimized and employees remain engaged. In industries that rely on performance-based pay models, such as healthcare, shifting incentive structures can be particularly challenging. Moving from annuity-based earnings (farming model) to models that emphasize new business development (hunting model) can create uncertainty, requiring thoughtful planning and structured execution.
This article explores how sales compensation drives cultural and strategic transformation, the importance of change management in pay model shifts and best practices for healthcare organizations implementing these transitions.
How Sales Compensation Drives Cultural and Strategic Transformation
Sales compensation serves as more than just a financial mechanism—it is a powerful tool for shaping employee behavior and reinforcing cultural shifts. When leadership decides to pivot toward a new business development model, sales compensation adjustments ensure that sales teams align with this shift and adopt behaviors necessary for long-term success.
In many industries, legacy sales compensation structures rewarded sellers based on recurring revenue streams, often providing annuity-based earnings that did not require significant effort to maintain. While this approach fostered financial stability, it often led to complacency, discouraging sellers from actively pursuing new opportunities and expanding market reach. When organizations move away from this model to focus on pipeline generation and customer acquisition, they must revamp their sales compensation frameworks to motivate these behaviors.
For example, in healthcare sales, it has become increasingly common to transition the sales compensation program from annuity payouts to new business bookings one. By tying earnings directly to new customer acquisition rather than legacy accounts, healthcare companies encourage sellers to prioritize lead generation, prospect engagement and deal execution over passive revenue maintenance.
This incentive shift drives a fundamental transformation in how sales professionals approach their roles. Instead of relying on existing client bases, sellers must actively build relationships, expand their prospecting efforts and refine their selling strategies to succeed under the new model. Sales compensation design ensures that transformation is not just a strategic decision at the leadership level, but rather an actionable and measurable shift that reinforces behaviors necessary for sustained business growth and competitiveness.
The Importance of Change Management
While sales compensation changes can effectively drive transformation, their success depends on strong change management frameworks. Employees must understand why a shift is happening, how it affects their role and what steps they need to take to succeed under the new model. Without structured change management, even well-designed sales compensation plans can lead to confusion, resistance and disengagement.
One of the most critical aspects of change management is employee engagement and support. When healthcare companies change their sales compensation models, employees often experience uncertainty or frustration, especially if their previous earnings structure provided familiarity and above market payouts. To ease the transition, organizations must implement training programs, leadership coaching and phased implementation strategies that reinforce new expectations and workflows.
A bridge program, for example, can serve as a temporary support mechanism, providing financial stability as employees adjust to new performance-based incentives. Structured transition plans allow individuals to develop necessary skills, adapt their prospecting techniques and build confidence in the new sales approach while limiting employee financial risk.
Beyond financial considerations, successful change management requires consistent communication, reinforcement mechanisms and direct involvement from leadership. Employees need clear messaging on why the change is occurring and how it benefits them individually and collectively. Healthcare organizations that proactively manage change minimize disruption, foster adaptability and establish transformation as a long-term success driver.
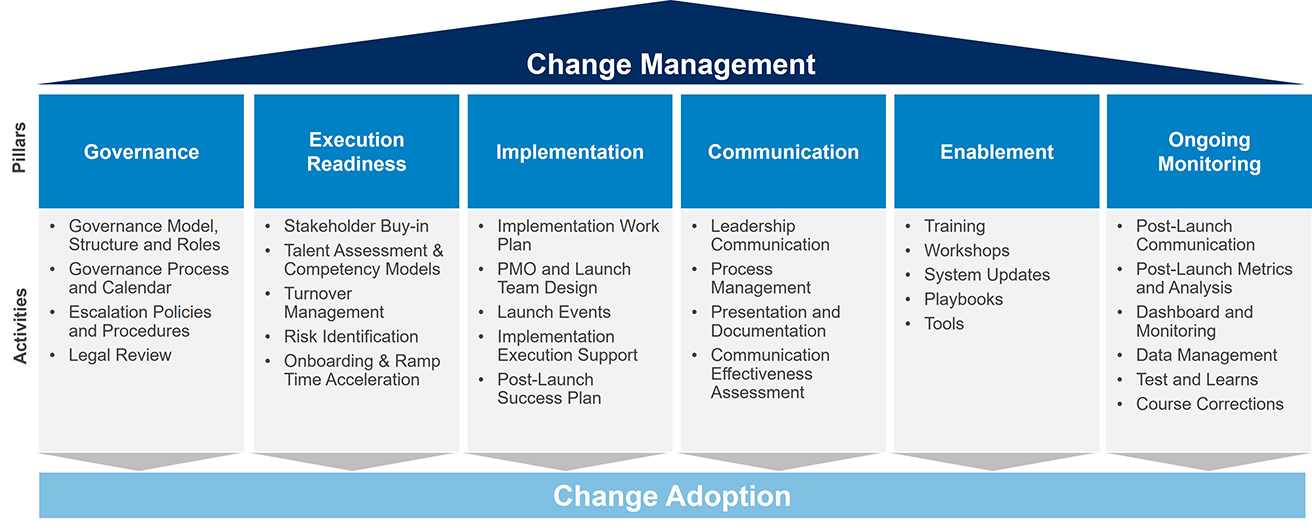
Often, a clear framework, like the one described below, can help ensure alignment and focus on the change management and adoption task at hand: