Should You Tie Customer Success Managers to Sales Incentives?
“As a service” (XaaS) business models offer customers flexibility and provide companies with an attractive stream of recurring revenue. Most software companies have already transitioned from perpetual to subscription sales. The business case for these models often relies heavily on “out-year” revenues in the form of upsell, cross-sell and renewal sales. For every $1 of annual subscription sales, best in class software companies realize $8-$10 in “out year” revenue (subscription revenue from years two through five). To retain and expand subscription revenue in a cost effective manner, winning companies deploy a customer success function.
As the role of customer success manager (CSM) becomes more commonplace, questions arise: What is the focus of the role? Should the CSM carry a quota? Is the role eligible for sales incentives? What type of sales compensation plan is best?
Four Types of Customer Success Manager
The Alexander Group (AGI) polled 25 software clients about their CSM roles at our recent XaaS Symposium in August. While Customer Success practices vary widely, AGI identified four primary CSM job types. How to manage performance and pay depends on the type of CSM role.
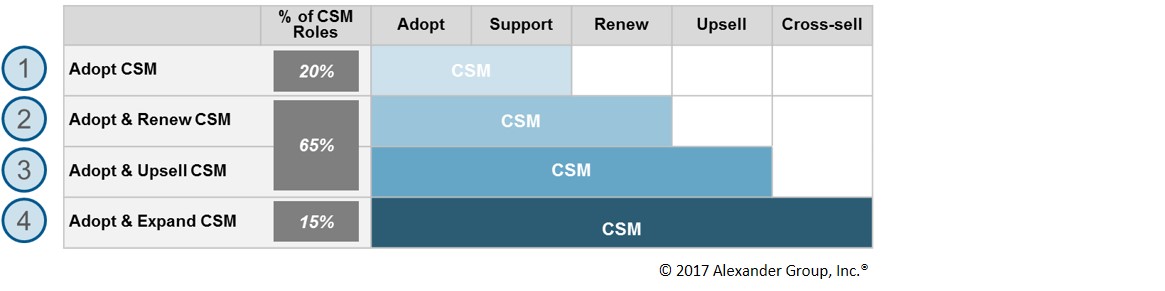
- Adopt CSM: As the name suggests, this CSM focuses on driving adoption and usage. The strategy for this role is “take care of the customer and more business follows.” The main performance measures are 1) usage (# of activated licenses, # of logons, user time & frequency, etc.) and 2) customer satisfaction (typically NPS). This role may or may not be eligible for the sales incentive plan depending on the company philosophy for incentives. Some consider this role the purest form of CSM and pay only a base salary. However, most companies place this role on the corporate bonus plan or a sales incentive plan with a pay mix of 90/10 or 95/5. This role may cover a territory with many customers, a portfolio of assigned accounts or provide dedicated focus to one key or strategic customer. In some cases, companies monetize this role and the customer pays extra for this premium service.
- Adopt & Renew CSM: This CSM performs similar tasks as the Adopt CSM with the added responsibility of driving renewal sales. In theory, the good work put against adoption helps ensure the renewal sale. As this role carries sales responsibility, it is eligible for sales incentives. Primary plan measures are one or more of the following: usage, customer satisfaction and renewal sales. The pay mix ranges from 80/20 to 95/5 with 90/10 the average.
- Adopt & Upsell CSM: This CSM is very similar to #2 with the added responsibility of upselling, which includes the sale of additional licenses, features, functionality or services related to the currently purchased service. These CSM roles carry progressively more sales responsibility. Thus, this role is eligible for sales incentives and typically has a more aggressive pay mix ranging from 70/30 to 80/20. Rather than tying incentives to softer measures like usage and adoption, plan measures include 1) upsell revenue, 2) renewal revenue and 3) client satisfaction. Upside earnings opportunity is also higher for this role given the more aggressive mix.
- Adopt & Expand CSM: This CSM role is similar to #3 with one key difference: it also cross-sells. Cross selling is the sales of related or unrelated products or services the company offers. This is an important distinction because it entails representing new and different offerings, and may entail calling on different buyers in the account. In its fullest form, this CSM role takes on the same role as a traditional account manager. This CSM is a “farmer” assigned to many accounts and is responsible for selling across product lines and buyers. This role is eligible for sales incentives, with pay mix ranging from 60/40 to 80/20.
The CSM role often works closely with an account executive or account manager and is not solely responsible for either upsell or cross-sell but often is the “point of the spear” in identifying these opportunities. There are many permutations of the CSM role, and it is important to match the plan type and quota responsibilities to the role.
Determining the Right CSM role for an Organization
The right CSM role (or roles) depends on the organization’s go-to-customer strategy and the way your target customers buy. If the offering lends itself to a “land and expand” model, consider deploying an Adopt & Upsell CSM or Adopt & Expand CSM. If the initial “land” is typically a major, multi-year contract, then the Adopt CSM is more appropriate. The CSM function plays a critical role to drive not only customer success (and satisfaction), but also renewal, upsell and cross-sell revenues. Highly functioning customer success teams drive significant sales at a fraction of the cost of traditional sales teams.
The Alexander Group provides consulting services to companies building out their Customer Success organizations. For more information, visit Alexander Group’s Technology practice.